If a vegetable variety has not left its position for over 80 years and has not been superseded by numerous successful developments of modern breeders, it means that it has enduring valuable qualities and a powerful margin of safety. Read all about late Moscow cabbage in the article.
Description and characteristic
This cabbage cultivar, which is now popular both in large vegetable farms and in rural farmsteads, was bred in the USSR in the 1930s. Actually, then vegetable growers developed the cabbage variety Moskovskaya late 15, and 20 years later this line was supplemented by the variety Moskovskaya late 9. Bearing the same name, with the exception of digital indices, both varieties are extremely similar, differing only in earlier ripening and shorter stump characteristic of Moscow late 9. They are more like varieties within the same variety.
The characteristic features of Moscow late are expressed:
- very spreading leaf outlet, often exceeding 1 m in diameter;
- oval wrinkled leaves of a greenish-gray shade with a slight coating of waxy properties;
- long leaf stalks and coarse veins on the surface of the leaves;
- large size and high density of heads of heads having a flat-circular shape and a white-yellow color in section;
- a high outer stump, reaching 0.3 m, and an average length of the inner;
- a large weight of heads of cabbage, on average 5 kg, but capable of reaching 15 kg under favorable conditions, which is why people call this cabbage “pudovka”;
- high productivity of up to 900 centners per 1 ha;
- yield of marketable products up to 97%;
- good keeping quality.
Did you know? In fact, a cabbage head is not a concentration of many leaves in one fork, but a huge wintering bud, which next year, sprouting, produces leguminous fruits with seeds.
Late Moscow cabbage 9
This variety is distinguished by:
- late ripening within 125-140 days;
- dense flat-headed heads of cabbage with an average weight of up to 8 kg, which under favorable conditions reach a mass of 15 kg;
- low poker;
- high palatability;
- universality of application;
- a shelf life of up to 8 months;
- the susceptibility of heads to cracking;
- ability to withstand the disease keel.

Late Moscow cabbage 15
This first variety of Moscow late cabbage is characterized by:
- late ripening within 142-160 days;
- large and tight heads of flat-round or round shape, reaching an average weight of up to 5 kg, but capable of gaining weight up to 15 kg;
- high gastronomic qualities;
- universality of application;
- external stump reaching 0.3 m in height;
- high productivity, sometimes exceeding 1 ton per 1 ha;
- the ability to withstand the disease keel;
- good portability of transportation;
- good keeping quality;
- heads of cabbage not prone to cracking.

Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- Based on the above features of Moscow late cabbage, its advantages include:
- good yield;
- density and juiciness of forks;
- the sugar content of the forks and the high content of ascorbic acid in them;
- almost simultaneous ripening of forks;
- high taste when pickling;
- lack of signs of cracking in heads of cabbage;
- good keeping quality;
- successful resistance to the disease keel.
This cabbage variety has no serious shortcomings, otherwise it would not have lasted more than 80 years. Some problems for vegetable growers are caused by a high stump, which sometimes does not withstand the severity of a large head of cabbage, due to which it falls to the ground. We have to high up the plant and even put props under it. Also, not everyone needs the need, because of large forks of cabbage, to devote large areas under it for the plot and at the same time abundantly water the plants.
Did you know? In the world today, there are about a hundred different types of cabbage, belonging to only three varieties of this crop in the form of cabbage, colored and leafy. And the most common are not at all familiar to us white cabbage varieties, but red cabbage, Peking, broccoli and cauliflower.
Optimal landing times
With the exception of the southern regions, the late-ripening cabbage variety, to which Moscow Late belongs, is grown using seedlings. And since by the time the seedlings should be planted in open ground, its age should be about 40 days, which means that seeds must be planted in the ground from late March to mid April, depending on the climatic conditions of the region. Experts recommend that by the time of planting in open ground seedlings have a height of about 0.2 m and up to 6 true leaves on the stem.
Cultivating varieties
There are no special differences from the cultivation of other late ripe cabbage varieties in the variety under discussion.
Seed preparation
The quality of the crop depends on the quality preparation of seeds for sowing. Before sowing cabbage seeds, you must:
Before sowing cabbage seeds, you must:
- Place in water heated to + 50 ° C for 15 minutes.
- After that for 1 min. immerse in cold water.
- Then, withstand in a mixture of trace elements dissolved in water for half a day.
- Next, thoroughly rinse the seeds in clean water and place them in the refrigerator for 24 hours on the lower shelf.
- After that, dry the seeds and begin to plant them in the prepared substrate.
Growing seedlings
The process of growing seedlings proceeds as follows:
- Small cabbage seeds are planted in moist soil no deeper than 1 cm.
- Then the containers in the form of plastic, cardboard or peat pots, as well as peat tablets or small boxes are covered with a transparent film and taken to a room with a temperature of about + 18 ° C.
- With the advent of the first sprouts, seedlings are watered, provided with bright light and can withstand at day temperature from + 14 ° C to + 16 ° C and at night temperature up to + 10 ° C.
- As the seedlings grow, it is necessary to feed it with complex fertilizers a couple of times, combining this process with watering, so as not to burn the delicate roots with chemicals.
- After the appearance of half a dozen of these leaves, seedlings can be planted in open ground.

Transplanting seedlings into the ground
The cabbage plot is prepared ahead of the fall, seasoned with organic and mineral fertilizers. It should be a sunny place dominated by slightly acidic or neutral loamy soils. Acidic soils are not suitable for this crop.
Seedlings are planted in excavated and buried soil at a distance of 0.8 m from each other, leaving as much space between the rows. After planting seedlings, beds should be well moistened.Important! It is categorically not recommended to plant cabbage in areas where representatives of cruciferous crops have grown for the past 3 years.

Plant care
Agronomic techniques when caring for Moscow Late practically do not differ from similar actions when growing ordinary cabbage.
Watering and feeding
This vegetable, being a moisture-loving crop, requires regular and plentiful watering. This is especially true in September, when there is an active accumulation of the mass of forks. But at the same time, the sprinkling method should be avoided, in which the ingress of water on the plant provokes cracking of the forks. The most favorable under these conditions is drip irrigation.
Large heads of this variety, for their development, in addition to sufficient moisture, require enhanced fertilizing with fertilizers. During the planting of seedlings in the soil, up to 40 g of urea and the same amount of nitrophoska are introduced into the hole, in addition, wood ash is added to the soil at the rate of 1 liter per square meter. m. In the summer and at the very beginning of autumn, the plant is fed with potassium sulfate and monophosphate in an amount of up to 20 g per square meter. Fertilizing is carried out during irrigation, dissolving fertilizers in water, in three doses with an interval of a decade. In addition, during the season with an interval of 2 weeks, top dressing is carried out using infusion of mullein or bird droppings at the rate of 1 liter per 1 sq. M.
Important! Approximately from the second decade of September, top dressing and watering of cabbage must be stopped.
Loosening and hilling soil
So that the crust formed on the soil after each watering does not interfere with the access of oxygen to the root system, it is necessary to loosen the soil around the plant after watering or after rain. The frequency of loosening can be significantly reduced by mulching the soil with hay, straw and rotted sawdust. However, this technique does not eliminate the need for hilling.
As already mentioned, this cabbage variety has a rather high stump, which may not withstand the weight of the head of cabbage, so during the season at least 3 times it is necessary to dig up the soil to the forks. For the first time, this operation is carried out a month after transplanting seedlings into the soil. Then they monitor the growth rate of the poker, and when the forks rises several centimeters above the ground, they carry out an earthing up.

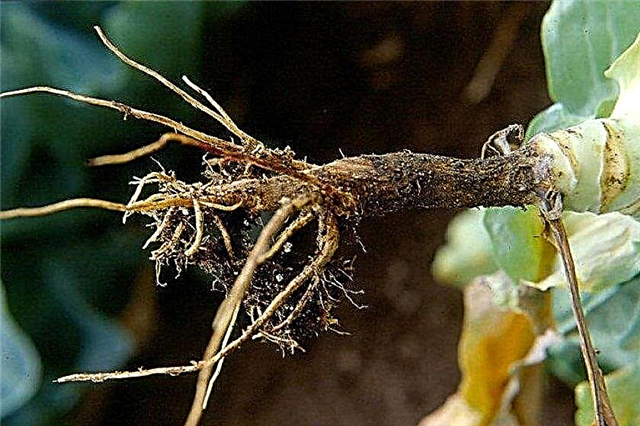
Diseases and Pests
For all its resistance to the disease, Kilo Moscow late cabbage is not immune from other diseases, as well as from pest attacks.
Most often, this cabbage variety is affected:
- black leg, which, as a rule, affects seedlings and seedlings, turning their stem into dark and watery, which soon leads to its decay;

- downy mildew, most often manifested in greenhouses, but with excessive moisture, can also occur in open ground, making the affected cabbage leaves inedible;

- mucous bacteriosis, which in an excessively humid atmosphere manifests itself with wet mucus on the surface of the fork, which leads to rotting of the vegetable and deprives it of consumer qualities.
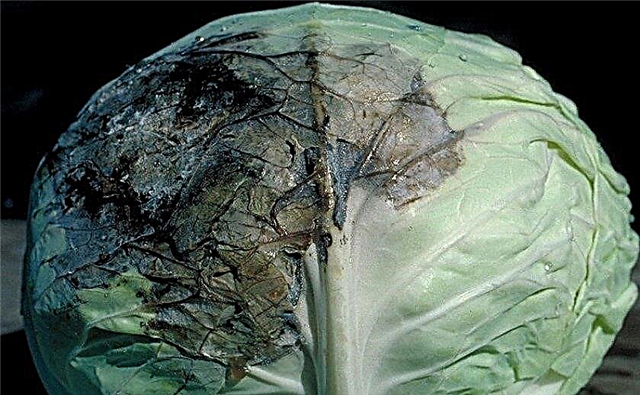
All these diseases are effectively controlled through biofungicides in the form of, for example, Fitosporin, Planriza, or Binorama.
Of the pests, this cabbage variety is most often attacked by:
- cruciferous fleas, which are small and very jumping insects, which, making a lot of tiny holes in deciduous coverings, render a significant part of the crop unusable;
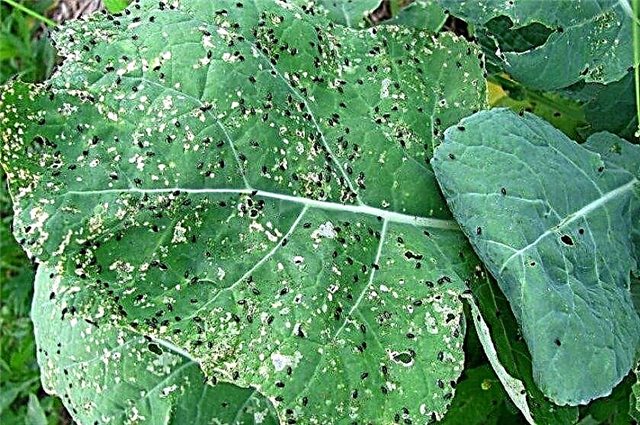

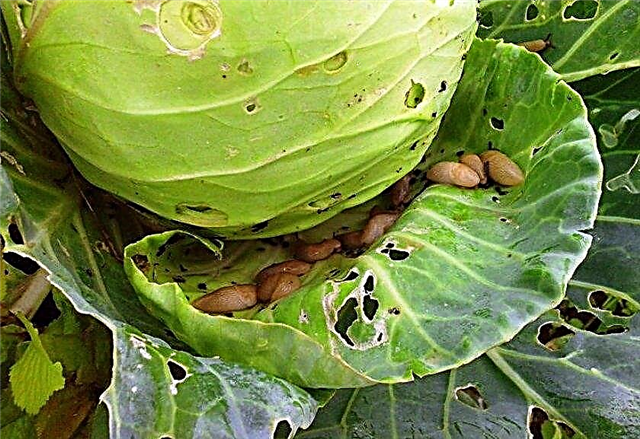
- slugsthat gnaw through the forks and make them unfit for storage;

- cabbage flies, the larvae of the spring and summer variants of which affect the root system of the plant.

Pest control by folk methods, as well as insecticides such as "Anabazin-sulfate" and "Bitoxibacillin." Against slugs, the Thunderstorm drug is effective.
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting of late Moscow cabbage is determined by the climatic conditions of a particular region, but most often this occurs in mid-October. The degree of maturity of the fork is determined by its compression with his hands. Hard and firm heads are ready for harvest. It is preferable to harvest in cool weather, which, according to experts, extends the storage time of cabbage.
Forks are pulled out of the soil and allowed to lie on the ground for four days, until the integumentary leaves subside. The field of this is removed and the outer poker is cut, leaving a couple of centimeters on the head. The densest forks are sent for winter storage, and the rest go for fermentation. Heads of cabbage are stored on wooden shelves or racks, where they are located in one row. Recently practiced wrapping forks in a cling film.
The late Moscow cabbage variety, which has successfully stood the test of time, is currently not only not losing ground against the backdrop of new developments by modern breeders, but is also expanding its presence in large vegetable farms and in small household plots.





















