Fir trees grown in private gardens suffer from diseases and pests as well as wild crops, so the successful cultivation of such trees largely depends on the correctness of the care organized for them. What exactly needs to be prepared in such cases, and how to quickly get rid of trouble when defeated conifers with popular diseases and pests - read on.
Causes of Disease
There are many reasons for the development of diseases or the spread of pests on spruce, but the list of the most common causes includes the following:
- non-observance of crop rotation rules and planting of coniferous seedlings in places of mass destruction of plants by diseases and pests in the past;
- waterlogging and waterlogging of the site;
- insufficient monitoring of the condition of the spruce (even a small pest damage in the future may become the basis for the development of one or more ailments of the needles or bark of the culture);
- improper selection of the cultivation site, with excessive or vice versa insufficient lighting of the site;
- violation of the recommendations for caring for the soil under certain varieties of spruce (if plants are not classified as disease-resistant, especially thickening of the near-stem zone by weeds should not be allowed);
- incorrectly selected fertilizers for top dressing (potassium-phosphorus compounds help to strengthen the immunity of spruce, while nitrogen-containing compounds are preferably used in a minimal amount).

Common diseases and their treatment
For spruce, almost all the same diseases are dangerous as for other coniferous crops, therefore, every gardener should be aware of the features of the manifestation and further elimination of gray rot, shute, fusarium, rust, bark necrosis, which are not in vain recognized as the most famous.
Did you know? Spruce needles contain a lot of vitamin C, which was appreciated in the XVIII century. Mariner James Cook. Coniferous wine based on the plant helped his team deal with scurvy.
Gray rot
Gray rot on spruce appears due to the ingestion of Botrytis cinerea fungus, which affects mainly the ground parts of young specimens. With the development of the disease, all shoots turn gray, brown or blacken, covered with conidia similar to a layer of dust.
As the spruce grows, there is a re-reflection of the healthy areas from the sick, due to which the trees very soon lose their appearance and weaken. Usually, gray rot affects plants planted in overly dense plantings, with limited light and air permeability.
As a fight against the disease, a solution of copper sulfate and special fungicidal preparations (for example, “Skor”) are used, but it is necessary after removal and burning of all affected branches. For early spring prophylaxis, the branches of coniferous plants are sprayed with Bordeaux liquid or a solution of the same “Skor”, only in half dosage.
Schütte
Schütte is another popular coniferous fungal disease caused by the fungus Lirula macrospora (common shute) or Lophodermium piceae (lowland shute). They can be amazed by the most different types of fir trees, the needles of which become brown or red-brown in summer, and in its lower part the fruit bodies of the mushroom form in the form of elongated, flat or slightly convex black pillows, stretched to half the length of the surface of the needles or even further.

In the lowland variety of the disease, fruit, round-oval bodies of black convex pads form on both sides of coniferous plates. To eliminate the problem, as in the first case, it is necessary to destroy all the affected parts of the tree, and spray the remaining shoots with copper-containing preparations and compounds with the presence of copper (“Abiga-peak”, Bordeaux mixture, lime-sulfur broth and “Khom” are suitable). The same compounds can be used to treat the spruce crown in early spring for preventive purposes.

Fusarium
Fusariosis is a dangerous fungal disease not only for conifers, but also for fruit or other ornamental crops. Its causative agent is a fungus of the genus Fusarium, which enters the tissues of a healthy plant from infected soil or plant debris located on it.
Important! When using the “Kartotsid” product, be sure to wear gloves and cover your face with a mask to prevent toxins from entering the skin and respiratory tract. The same applies to the use of less toxic chemicals.
First, the affected needles of the spruce acquire a grayish color, then become more brown and, ultimately, completely dry out. Gradually, several affected branches lead to a massive spread of the disease in the tree, as a result of which the culture loses its decorativeness and dies.

With a strong infection with fusarium, the only right solution is to destroy (mainly by burning) the affected specimen, but if the signs of the disease appeared only on some shoots, you can try to save the spruce. To do this, after removing the diseased branches, spray the remaining shoots with the fungicides "Fundazol", "Topsin-M" or "Previkur", dissolving the selected preparations in water at the rate of 2 g per 1 liter of liquid.
To consolidate the effect, such treatment is carried out twice, with an interval of 2-4 weeks. After treatment, over the next few years, prophylactic treatment in early spring is required, for which the same drugs are suitable, but in half dosage.

Rust
Rust (in the later stages of development “spruce wereter”) is mainly a summer disease of spruce, which in the initial stages manifests itself in orange-yellow bubbles on the needles of the plant. After some time, a yellow powder (fungal spores) appears from the bubbles, which, falling into the plant tissue, leads to their destruction.
Outwardly, this is expressed in the yellowing and drying out of the needles and shoots, they become as if rusty, which is why the disease got its name. With the mass spread of rust on one spruce, it will be difficult to save the tree, so most gardeners recommend immediately removing it with the root, thereby preventing the spread of the disease in the garden.
If the lesion sites are not extensive, spraying with fungicidal preparations such as Bordeaux mixture, copper oxychloride, the Abiga-Peak systemic fungicide or any other similar agent can help. As in previous cases, the effect of their use can be enhanced by repeated treatment at least through 2-3 weeks after the first spraying.
Did you know? Spruce plantings are able to change the climatic conditions of the external environment. So, in the summer period it will be cool in such a forest, and in winter the temperature in the spruce is slightly higher than outside.
Necrosis of the cortex
Necrosis of the cortex is also an ailment of fungal origin, the causative agent of which is the fungus Sphaeria pithyophila Fr. The first signs of the disease usually appear in the second half of summer and are noticeable on the branches of the lower tiers located closer to the soil surface. If the spruce grows in shaded areas with high humidity inside the crown, then over time the disease moves higher, sometimes up to the upper tiers of the tree.

With a significant defeat of the bark, the branches dry out, and the young plant may even die, since often the fungus affects not only the bark, but also the needles or even the buds of the spruce. Black perithets of the fungus erupt through the bark of the affected branches, which can be compared with small dark warts: single or small groups located on the branches.
For prevention and treatment, at the initial stages of the spread of the disease, copper-containing fungicidal preparations, as well as coating the tree trunk with garden varnish or paint, will be appropriate. Increasing the resistance of spruce to this ailment can be achieved through the use of micronutrient fertilizers and immunostimulants, which are introduced under the plant every year in early spring.

Pests and the fight against them
Pests of spruce are one of the main causes of death of trees, both during garden cultivation of conifers and in open nature. The common harmful insects of this plant include spruce aphids, hermes, mealybugs, bark beetles, spider mites and beetle eaters, although the spruce barbel does no less harm. Each of the pests has characteristic features, taking into account which gardeners select effective methods for solving the problem.
Aphid spruce
This pest can be detected by yellowing and drying of the needles of the plant, as well as by the appearance of a large number of ant nests around it. To see the insects themselves, you just need to raise the branch and look at the inside, where they densely cling to the surface. Their presence will not be able to destroy the spruce, but, sucking the sap from the tree, the aphid significantly worsens its appearance and violates the general decorative effect.
Their presence will not be able to destroy the spruce, but, sucking the sap from the tree, the aphid significantly worsens its appearance and violates the general decorative effect.
In case of a severe defeat, remove the affected shoots and spray the remaining branches with an insecticide such as Actara, and then repeat the spraying using the Match and Dursban, keeping an interval of 2 weeks between all treatments.
Hermes
The first thing that catches your eye with a defeat of spruce with hermes is the curvature and yellowing of the needles, with sticky fluffy and snow-white neoplasms on the inside. At the ends of young shoots, galls in the form of cones appear almost immediately, which constantly grow, grow and acquire a crimson color.

Inside the affected shoot there can be up to 120 hermes larvae, and if you look closely, adult female pests will be visible next to the buds on the bark, and brown or yellowish-green larvae on the needles. It is the latter that are responsible for bending and drying out the shoots, with further shedding of needles and the death of the branches (usually occurs only in the second year after the pest is damaged).
You can get rid of insects by regularly removing all infected shoots and using systemic insecticides introduced under the root. Normal spraying in this case will be ineffective, since chemicals are not able to penetrate gall fluff. Examples of effective insecticidal formulations will be Decis, Actellik, Aktara and Iskra. By the way, they can be further used for preventive spraying of spruce stands.
Mealybug
Mealybug is a popular pest in the garden. This small sucking insect resembles an aphid outwardly, which also poses a danger to conifers. The yellow oval body of the vermilion is usually densely covered with white wax-like secretions, some of which in the summer also remain on the needles of young spruce, later forming peculiar pieces of “cotton wool”.
Important! In the issue of the effectiveness of the selected insecticidal composition, the feature of spruce care plays an important role, so some drugs used soon after foliar feeding of the plant may turn out to be ineffective, or vice versa, cause damage to the needles. For this reason, you will have to postpone the treatment if you have just fertilized the tree with liquid mineral fertilizers.
Sometimes they can be confused with signs of hermes activity, only worms leave much more fluffy traces. In such places, it is likely that the shoots of the plant will quickly die out, as the small pests in the “gun” quickly suck the juices from the tissues and cause the shoots to die.
In case of severe plant damage, in addition to manual removal of the mealybug and all branches affected by it, it will be appropriate to treat one of the effective insecticidal compositions: Actara, Biotlin, Calypso, or even Confidor, which is often sprayed with garden crops. You may have to change several of these drugs, the main thing is to find the most suitable solution and conduct a double treatment with a break between procedures of 7-14 days.
You may have to change several of these drugs, the main thing is to find the most suitable solution and conduct a double treatment with a break between procedures of 7-14 days.
Bark beetles
When coniferous trees are affected by bark beetles, the most noticeable sign of its presence will be a strong release of resinous transparent substances, which is evidence of the struggle of the plant with beet toxins. If the spruce does not have enough strength to defeat the "enemy", then soon a brownish flour will appear on the trunk or immediately below it, which spills out from the damage of the shoots located above.
In fact, these are small sawdust remaining outside after the bark beetle bites into the wood. To finally verify its presence on a particular plant, you can check for coniferous litter under the spruce, as well as pay attention to the detachment of the bark.

With a combination of all the above signs, it is possible to select with confidence a tool for combating bark beetle. The most effective chemical insecticidal preparations today include Bifentrin and Clipper, which are sprayed twice with a standard interval of 2-3 weeks.
In some cases, barrier control against bark beetles on spruce, involving the use of pheromone traps, will be no less useful. They will be especially appropriate for large areas of spruce plantations, since the substance used attracts beetles at a distance of 7 km. After pests densely encircle a plant with a trap and some neighboring ones, such spruce trees are removed and taken out of the site, removing bark beetles along with them.
When growing spruce in small private areas, this solution to the problem can be very dangerous, because the gardener risks being left without all the plantings. In such situations, it is better to use antiferomones that are dotted on single plants and repel harmful bugs from them. 
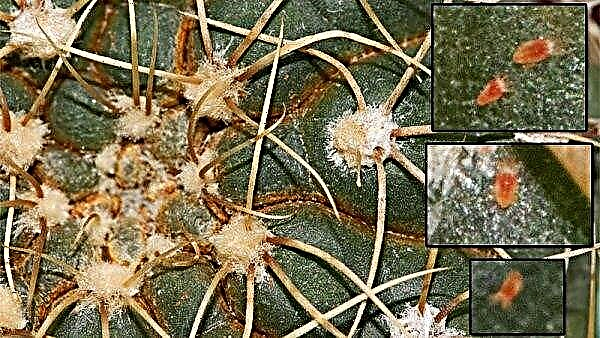
Spider mite
The presence of the spider mite on the spruce will be noticeable by the thin and rare cobwebs on the needles, as well as yellow spots on the surface, which subsequently lead to complete drying of the needles. During the summer, one female gives 3-4 generations of new insects, so if you do not take measures to destroy them in a timely manner, you can completely lose the spruce by the end of the summer.
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to spray spruce needles on young seedlings with cold water, thereby increasing the humidity level in arid and hot summers. However, in the event of the first symptoms of insect damage, it will not be possible to do without the use of drugs based on colloidal sulfur or more serious acaricides (for example, Fitoverm or Kleschevit).Important! The spider mite is clearly visible with morning dew. Its glare helps to see a thin web stretched on young shoots, along which the smallest ticks move, with a body length of no more than 0.3-0.5 mm.

Luboed
The presence of the beetle on spruce is expressed in the reddening of its needles and the formation of large resin funnels at the sites of introduction of insects into the stem of the plant. Mostly, old trees suffer from their presence, although with a massive invasion, recently planted Christmas trees can also be affected, on the trunks of which brownish flour will be noticeable in any case.

The most effective way to protect against the beetle eater is to remove the affected plant from the site and burn it further with the pest, but if there is little oil, you can use one of the insecticidal preparations: Inta-Vir or Tabu. With extensive plantings, pheromone traps are used, but the same rules apply as in the case of bark beetles: in small plots of land there is every chance of harming the vegetation.
Barbel spruce
This pest is presented in the form of a small beetle with an elongated body and a mustache thrown on its back, which served as the name for insects (in some species their length exceeds the length of the body of the beetle). When sprucing into the trunk of a spruce, spruce barbel leaves leave numerous moves inside, and when eggs are laid on the surface of the shoot bark, characteristic notches will be noticeable, as if they pressed a bark with a fingernail.
Compared to aphids or spider mites, this pest is not so widespread and enters private areas mainly along with infected planting material from spruce nurseries.
 It is better to deal with this pest by biological methods, attracting woodpeckers or swallows to the site of their natural enemies, but with the widespread spread of insects, it is unlikely that they can do without insecticidal drugs, the role of which may be one of the examples presented earlier.
It is better to deal with this pest by biological methods, attracting woodpeckers or swallows to the site of their natural enemies, but with the widespread spread of insects, it is unlikely that they can do without insecticidal drugs, the role of which may be one of the examples presented earlier.
Disease and Pest Prevention
Modern preventive measures to prevent the defeat of firs by diseases and pests are a much more profitable solution than the search for means to eliminate an existing problem.
Therefore, in order not to think then what to do when the pests are invaded or the oil is damaged by any disease, it is worth adhering to the following recommendations:
- always carefully inspect the planting material and buy it, only making sure the health of the seedling or seeds;
- timely remove dried, broken, damaged by diseases and pests branches, always covering the places of cuts with garden varieties or special paints;
- apply micronutrient fertilizers and immunostimulants to increase plant immunity;
- comply with crop rotation rules, avoiding planting fir trees next to unwanted neighbors, such as bird cherry;
- carry out pre-planting treatment of the rhizome of seedlings and use fungicides at the first appearance of signs of a particular ailment;
- to carry out annual spring preventive spraying of spruce stands with copper-containing preparations.

Special attention should also be paid to pre-plant soil treatment, which, if possible, should be calcined and shed with the systemic fungicide Trichodermin. To normalize the acidity level of the soil, it is useful to add dolomite flour and chalk to it, which will significantly reduce the likelihood of root rot.
In the autumn period, it is useful to perform a deep digging of the soil in the near-trunk zone, so that the larvae remaining in it freeze to the surface in the winter and do not cause new problems next year.
Of course, both larch and coniferous trees are not immune to diseases and pests, therefore it is not surprising that certain problems are encountered when growing spruce trees. With a proper approach to the issue of spruce care and timely prevention, a strange coating will not appear on the shoots of the trees, and the needles will not pour in, which means that the plant will retain its decorativeness and will delight the gardener with the appearance.