The right choice of potato variety has a big impact on the quantity and quality of the future harvest, so you need to approach this business responsibly. We offer you to get acquainted with the description of the best early varieties of potatoes.
The best varieties of early potato species
Early varieties of potatoes are divided into several varieties:
- super early;
- early ripening;
- early
- mid-early.
 They are not suitable for winter storage.
They are not suitable for winter storage.
The features of early potatoes are not only fast ripening, but also a thin peel, short shelf life at high temperatures. After storage, the tubers lose up to 8-15% of the mass due to moisture loss. Usually, early varieties are planted to be consumed in summer and autumn. Below is a description of the best varieties in each category.
Did you know? Potatoes were cultivated about 9 thousand years ago in the territory that Bolivia occupies today. The inhabitants of South America, in addition to eating tubers for food, also worshiped this plant, reckoning it among creatures that have a soul.
Ultra early
The earliest potato has the following characteristics:
- high level of resistance to the main characteristic diseases;
- high yields;
- shortened growing season.
Planting is carried out by heating the soil to + 8 ... + 10 ° C, approximately in the last weeks of April or the first weeks of May.
 Harvesting should begin when the peel is fairly dense.
Harvesting should begin when the peel is fairly dense.
The best among the ultra-early varieties for growing in suburban areas are the following:
- Timo. Suitable for growing in almost all regions. Productivity is 340-610 kg / ha. The fruits are delicious, suitable for any culinary purpose. The plant is well resistant to cancer.

- Riviera. Forms tubers of the correct form, which have an attractive appearance and can be used both for personal purposes and for sale. In the southern regions, this variety can be planted twice. It tolerates storage not bad. It has a high resistance to viral infections, a nematode and an average level of resistance to late blight.

- Karatop. It bears beautiful and tasty fruits weighing 80–130 g with small eyes. The plant is demanding on moisture. With prolonged drought, significantly reduces the quantity and quality of fruits. The crop is well stored for a long time.

- Ariel. The main feature of the variety is that after heat treatment, the pulp of the fruit does not darken. If you observe the recommended planting dates, you can plant the plant twice. Varieties Ariel do not curl leaves, he does not suffer from tuberous late blight, rarely affected by scab.

Experienced gardeners argue that early potatoes can be planted when buds open on birch trees and bird cherry blossoms.
Early ripening
Tubers of early ripening varieties usually contain a small percentage of starch, so after cooking they remain hard. Plants are planted in the first weeks of May. They are resistant to fungal infections.
Of the premature ones, the most popular are:
- Zhukovsky early. Since the variety tolerates cold well, it can be planted in mid-spring. He forms large tubers weighing 100-150 g, with white flesh that does not darken if cut, and does not boil. Plants well resist nematodes, scab, rhizoctonia. Do not suffer from drought. Their productivity is average.
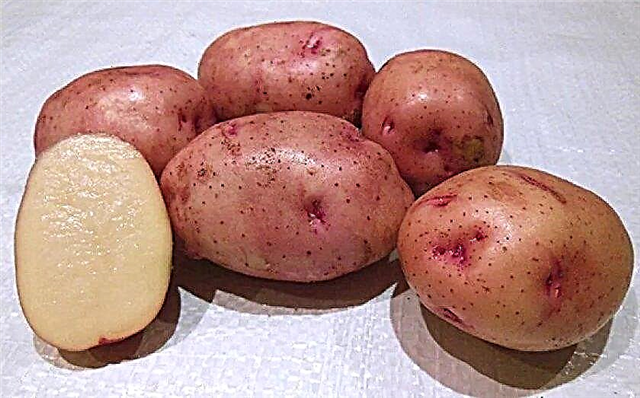
- Colomba. The Dutch variety, which shows high productivity - 224–442 kg / ha. The plant is not affected by cancer, nematode, rarely gets sick with scab and late blight. Fruits are large - weighing 85–130 g. When cooking, they scatter slightly. Their taste is high. Tubers can be stored for about 6 months.

- Bellarosa. Gives tasty tubers weighing 115–210 g. They have a pink peel, light yellow flesh. The variety is classified as high-yielding - one crop is 20–35 t / ha. Bushes well resist defeat by diseases. The first crop can be harvested in early July. In the southern regions, this potato is planted twice a season. The second crop is harvested in early autumn.

- Farmer. Ripe tubers reach a mass of 90–110 g. The starch level in the pulp is 9–12%. The yield of the variety is 200–230 kg / ha. Suitable for growing from seeds. It responds well to regular moisturizing and fertilizing. The plant shows resistance to cancer, nematode, late blight, viral infections. Tubers are characterized by good keeping quality.

Early
Among the early varieties, the attention of summer residents deserves:
- Izora. A table variety that produces large tubers - weighing 80–120 g, with good taste characteristics, white peel, light flesh that does not darken when cut. Bushes are resistant to cancer, viral infections and late blight. Productivity of the plant is 30–35 t / ha.

- Anosta. The main advantages of the variety are high productivity, beautiful, uniform shape and size of the fruit. Their taste characteristics are marked as good. The starch content is at the level of 14–16%. Tubers are great for cooking french fries and chips. Bushes well resist cancer, nematode, scab. The plant shows medium resistance to late blight.

- Impala. In this variety, mature tubers weigh 88–150 g. They have smooth skin, small eyes, and a light yellow inner part. The fruits have an attractive presentation and good taste, rated at 4 points out of 5. Their shelf life is estimated at 90%. Productivity is 367 kg / ha. Impala does not get cancer, is not affected by a nematode, and rarely gets infected with common scab and viruses.

- Red Scarlett. A high-yielding table variety with a maximum yield of 600 c / ha. Its tubers are oblong, with an attractive smooth reddish skin and light yellow flesh, weighing 80–130 g. They are well stored - keeping quality is 98%. The plant withstands the onslaught of nematodes, cancer, late blight of tubers. However, it is often prone to diseases such as scab, late blight, leafworm, and alternariosis.

Mid early
Mid-early varieties are characterized by high resistance to most infectious diseases, but are susceptible to late blight. As a rule, they give tubers attractive in appearance and excellent in taste, which are great for implementation.
In the medium early category, the following varieties can be called the best:
- Nevsky. Tubers of this variety are formed with yellowish skin, white flesh, weighing 90-130 g. The fruits acquire excellent boiled taste and do not boil. The yield of the variety is high - 1.5 kg per bush, 60 t / ha. The plant can tolerate drought and waterlogging without problems, resist late blight, scab, black leg. Tubers are less susceptible to bacteria, viruses and fungi.

- Elizabeth. It is characterized by increased productivity - 290–400 c / ha. Oval fruits with beige peel and white delicious pulp. The average weight of one tuber is 142 g. The starch level in them is 13–18%. Keeping quality is 93%. The plant is well resistant to viruses and scab pathogens, but is sensitive to alternariosis.

- Adretta. Planting is carried out in mid-May, harvesting in July. The benefits of the variety are delicious fruits. They have an average starch content of about 16%, a delicate yellow flesh that crumbles during cooking. The average weight of one fruit is 120–140 g. The high-yielding variety is 45 t / ha. It perfectly resists viral infections, is practically not affected by harmful insects, and can endure unfavorable weather. Sensitive to scab, late blight, blackleg, rhizoctonia.

- Santa. Tubers of this variety are distinguished by good keeping quality. They are large - reach a mass of 100-150 g, smooth, rounded, with a smooth yellow skin and yellow flesh. Due to the even form and attractive appearance, they are suitable for implementation. A little starch in them - about 10-14%. The yield of a variety, depending on where it grows, can be 270–570 kg / ha. The plant resists damage to the main diseases of the nightshade family.

Features of planting early varieties
Potatoes should be planted when the soil warms up to + 8 ... + 10 ° C to a depth of 10 cm. Planting time will depend on the growing region and climatic conditions that are typical for it. But, as a rule, landing is carried out not earlier than mid-April.
In warm regions, when cultivated under a film, early varieties can be planted even earlier - at the end of March. Then the first harvest can be expected in May. For planting and cultivation to be successful, it is necessary to properly prepare the soil and planting material.
Bed preparation
Potato land is being prepared since autumn. The preparation process is:
- thorough cleaning of plant debris;
- deep digging;
- plowing to a depth of 22–25 cm;
- making mineral (urea) and organic (manure, ash) fertilizers;
- the formation of high beds.
Important! For growing potatoes, you must choose a well-lit area with fertile soil. The beds are located from the northwest to the northeast.
If no fertilizer was applied in the fall, this is done in the early spring, a few weeks before planting. Dry humus (1 l) and wood ash (1 handful) are added to each well. It will also be necessary to saturate the soil with minerals: nitrophos (1 tbsp. / 1 well), ammophos (1 tbsp. / 1 well) with dolomite flour mixing (0.5 tbsp. / 1 well).
Tuber preparation
Only fruits that have sprouted are suitable for planting. It is necessary to select those for which they are strong, with a maximum length of 1 cm. If roots have formed on the sprouts, this will only be a plus.
To sprout potatoes, you need to make a circular incision on it and place it in a room with diffused lighting, air temperature + 12 ... + 15 ° С in the daytime and + 6 ... + 8 ° С in the night, humidity 90–95%. Under such conditions, tubers germinate in less than a month.

If you need to speed up the process of germination, then you can resort to the following manipulations:
- put the fruits in moist sawdust or peat treated with a solution of copper sulfate (2 g / 1 l of water), additionally cover the planting material with a layer of wood ash;
- place the tubers in 3-liter glass containers that need to be installed on the sunny windowsill.
Damaged and rotten fruits should be discarded immediately before planting.
Landing technology
The recommended planting scheme for early potatoes is 60x70 cm. A distance of 25-30 cm should be observed between plants. So, 5-6 bushes will appear on 1 m². The depth of the tubers is 6-8 cm. Planting is carried out in previously dug grooves or in holes on the ridges. After placing the tubers, they are sprinkled with soil, and then loosen it with a harrow or rake. This will prevent the formation of lumps and hard crust.
Important! The success of growing potatoes and the abundance of the crop is greatly influenced by the observance of crop rotation rules. The best predecessors are siderates, cucumbers, legumes, onions, cabbage, carrots, peppers, beets. The worst are potatoes, tomatoes.
Cultivation and care
Potato care involves the following procedures:
- hilling;
- watering;
- loosening;
- weeding;
- top dressing;
- preventive spraying against diseases and harmful insects.
Hilling. This procedure allows you to protect seedlings from May frost. It is produced when the seedlings grow 10–15 cm high. The second hilling is carried out for sprouts 15–18 cm high. Plants are cultivated with moist soil.
Watering. Humidify potatoes infrequently - with an interval of 7-10 days. Most moisture is needed during the formation of tubers. For 1 m², the use of 40-50 liters of water will be required.
Loosening. Each watering and precipitation is accompanied by loosening. This procedure avoids the formation of a hard crust on the soil surface, and also improves its air and moisture conduction.

Weeding. The beds need to be kept clean. Weeding is often carried out - starting from 6-7 days after planting and before harvesting.
Top dressing. To fertilize potatoes during the growing season or not, each owner decides for himself. If there is a need for top dressing, then for the first time it is done 2-3 weeks after planting. Urea (15 g / 1 m²) is used. The second time, before budding, make potassium fertilizers. They also use a scheme of three top dressings: fertilizer Effecton, superphosphate and potassium sulfate.
Prevention of diseases and pests. The main enemy of potatoes is Colorado beetle. Insecticide spraying of plantings will help prevent a parasite from entering the site: “Cruiser”, “Aktara”, “Tanrek”, “Corado”, “Commander”, “Zenith”. In order not to harm the plant, you should clearly adhere to the dosage specified in the instructions. To repel pests in the immediate vicinity of potatoes, wormwood, marigolds, dill, and calendula are planted.
Since early varieties are resistant and susceptible to various diseases, the schedule of preventive treatments for each of them will be special.
Important! The use of covering material during the cultivation of early potatoes increases the yield by 10-15%.
Ripening time
Each of the varietal varieties differs in terms of ripening, i.e., the period that passes from planting to harvesting. When digging potatoes of different types, you can determine by reading the ripening time.
So, super early varieties are ready for harvesting 40-60 days after planting. The ripening time of early ripening varieties is 50-60 days. Harvesting early potatoes begin after 61–70 days. Mid-early varieties begin to be excavated 71–90 days after placing the seeds in the ground.
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting is carried out at the moment when the leaves of the lower tier begin to turn yellow and flowering ends. For personal purposes, digging is carried out gradually, until July-August. Keeping tubers in soil later than August 20 is not recommended.
Tuber seeds are harvested a little later than the first digging is done. They are put in bags and placed for 1-2 weeks in a room with diffused lighting.
 The shelf life for tubers depends on the variety. Some can be stored for 6 months, others are advised not to store at all, but to use it shortly after harvest.
The shelf life for tubers depends on the variety. Some can be stored for 6 months, others are advised not to store at all, but to use it shortly after harvest.
Potatoes are not immediately stored. They put it in bags and put it in a dark place with good ventilation and a temperature of + 15 ... + 20 ° С. After 1-2 weeks, it is inspected and discarded unsuitable for storage specimens. After that, the tubers are transferred to the storage with the following parameters: air temperature - +4 ... + 6 ° C, air humidity - 90–95%, good air circulation. Storage facilities are pre-disinfected.
Did you know? After the delivery of potatoes to Europe in the 16th century, they did not eat it, considering it a decorative and poisonous plant. The recognition of its nutritional qualities was due to the work of the French agronomist Andre Parmantier. In 1772, the Faculty of Medicine of Paris announced the edibility of tubers.
Breeders made sure that summer residents had a large selection of early varieties of potatoes. Landing and caring for them will not be difficult. In some varieties, 2 crops can be harvested per season.




























