Siberian larch is not afraid of polluted city air, therefore it is often used in landscaping park areas. Owners of spacious garden plots also pay attention to this tree, being interested in the intricacies of its cultivation.
Botanical Description
The plant is ubiquitous in the northern territories of Russia: in Siberia, the Urals, in the Altai Territory, is less common in the middle lane and central regions. Under natural conditions, grows next to fir, pine and other conifers.
The tree reaches 40 m in height and 1.8 m in girth of the trunk. Young specimens form a pyramidal crown, their bark is the color of ripe straw. As it grows, the shape becomes round, the color of the trunk becomes a gray-brown hue with pronounced grooves. Annual shoots are straight, the needles on them are collected in a spiral, yellow-green tone. Perennial branches are decorated with needles of a light green color, growing in bunches. The needles are soft, narrowly linear, 15–45 mm long.Did you know? From a resinous substance secreted by larch tissues called gum, natural chewing gum is produced. The product is used for dental purposes: for the treatment and prevention of oral diseases.
The dioecious culture blooms in April or May. Female inflorescences are colored in purple, and male inflorescences are yellow. The flowering period lasts 1.5–2 weeks and coincides with the blooming of needles. Larch belongs to coniferous crops, but annually drops needles in the autumn.
In September, elongated cones ripen with scales located in 5-7 rows. At the beginning of development, they are painted in a bright red-violet tone, then brighten to a yellowish tint. The yellow winged seeds ripen in cones up to 5 mm in length.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among summer residents, larch is not in great demand, but in large areas of private land it is used in landscaping.
- Plant Benefits:
- frost resistance, grows even beyond the Arctic Circle, does not require shelter for the winter;
- unpretentiousness to soils;
- resistance to strong gusts of wind;
- all parts of the plant have healing properties;
- immunity to diseases and pests;
- thanks to volatile, it cleans the air.
- Disadvantages:
- late fruiting during artificial cultivation after 20-30 years of life;
- large sizes, takes up a lot of space;
- throws needles like deciduous crops.
Planting a plant
The best time for the procedure is autumn, when the needles have already fallen. A seedling will no longer waste energy on its nutrition and moisture supply. Success depends on the right choice of planting material. In addition, you need to prepare a place and a suitable substrate.

Site selection and preparation
Siberian larch can grow on rocky and swampy soils. Even young specimens are not afraid of the wind and sudden temperature drops.
And yet there are a few rules for successful cultivation:
- The site should be well lit.
- Groundwater runs below 2 m from the surface of the earth.
- Nearby there should not be a birch or elm, they are competitors for culture.
- The next plant is planted after at least 4 m.
 At the place of future planting, they dig the soil, adding sand for looseness in a ratio of 2: 1. As a soil fertilizer, you can use a three-year humus, adding 4-5 kg per m².
At the place of future planting, they dig the soil, adding sand for looseness in a ratio of 2: 1. As a soil fertilizer, you can use a three-year humus, adding 4-5 kg per m².
Seedlings selection
Planting material should be purchased in the nursery and only with a closed root system. A material with open roots has no chance of survival. A sapling under the age of 3 years is easier to adapt. It should have an even trunk, clean and smooth bark. Mandatory presence of developed skeletal branches.
Process technology
For a seedling, dig a hole twice as large as its roots. Before planting, the plant is carefully thrown out of the tank and the roots are soaked in the root stimulator “Kornevin”. The drug is diluted in a proportion of 1 g / 1 liter of water.
Important! To make sure that the seedling is rooted in the container, and not just transplanted, turn it over. Waking up soil means that the tree did not grow here.
Landing pattern:
- At the bottom of the pit, a mound is formed from half of the previously extracted earth, approximately to the height of the root system.
- Place a seedling on a hill, straighten the roots.
- After they are sprinkled with soil, gently shaking and tamping so that air voids do not form.
- It is necessary to ensure that the root neck is above the surface.
- After planting, it is watered, consuming a bucket of water, and the trunk circle is mulched with sawdust or straw.
Video: larch planting
After landing care
Beginners in gardening can make the mistake of caring for larch exclusively as a conifer. The plant belongs to this group, but, as was said in the description, the needles are discarded, like foliage in deciduous crops. This means that the tree needs to be given more attention than the pine or spruce.
Watering Rules
Siberian larch is resistant to weather conditions, but does not tolerate drought. This is especially true for young specimens up to 5-7 years. More frequent, 2-3 times a week, should be moistening the soil in the summer heat. In this case, it is important not to fill the tree trunk circle, so as not to provoke rotting of the roots. There will be enough water when the soil is moistened 20–25 cm in depth.
 An adult tree has a deep and well-developed root system. Watering for him is carried out 3-4 times a season, in the absence of precipitation more often.
An adult tree has a deep and well-developed root system. Watering for him is carried out 3-4 times a season, in the absence of precipitation more often.
To nourish the roots, it is recommended to add crushed mushrooms, since in nature crops live in symbiosis. In summer, at high temperatures and a small amount of rain, needles need to be sprayed. In dry air, burned by the sun, it turns yellow and loses its appearance.
Top dressing
The first 2-3 years, the fertilizer planted during planting is enough for the tree. Next, you need to feed the culture, as it needs strength for the annual restoration of the coniferous cover of shoots. However, a large amount of nitrogen is detrimental to the tree.
An ideal option for spring fertilizer is compost: it contains little nitrogen and a sufficient number of trace elements necessary for full development:
- magnesium;
- sulfur;
- calcium;
- iron.

Fertilizer is laid out in a layer of 3-5 cm in the near-stem circle, leveled with a rake. At the end of April, to stimulate flowering, coniferous plants are sprayed with a solution of wood ash 200 g / 10 l, adding 2 g of boric acid. The last top dressing is carried out 1–1.5 months before the onset of frost. Dry superphosphate granules of 50 g are scattered in the near-stem circle, spread with a rake and watered.
Mulching and loosening of soil
Ephedra love loose soil, so it is important after each watering to loosen the earth in the near-stem circle. The depth of immersion in the soil of a garden tool near a newly planted tree is not more than 10 cm. Simultaneously with the swelling of the soil, germinated weeds are removed. Parasitic herbs pull nutrients and moisture from the soil. In addition, their rapid growth thickens the tree trunk area, creating an ideal environment for the propagation of fungi.

Mulch helps to preserve moisture in the soil, the cleanliness of the trunk circle and protect the roots from overheating for longer. Shelter is fallen needles, sawdust or other natural material. A layer of 6-8 cm is enough, a thicker layer will not pass the air necessary for the roots.
Pruning
Larch will look beautiful and well-groomed if it is carried out correctly. Larch is one of the few plants that form the crown on its own. The tree does not like frequent pruning, it can respond to any disease. Therefore, it is not recommended to cut the Siberian conifer up to 5 years.
What does not hurt is sanitary scraps of broken, frozen branches. It is advisable to remove shoots that grow inside the crown or interfere with the main skeletal branches.Important! The forming haircut is carried out in stages: one tier - one year. If you trim a large mass, the tree will become sick and may not survive the winter.
Winter preparations
Adult plants do not need shelter; they perfectly tolerate gusty winds and lower temperatures to -40 ° C. Young specimens in particularly harsh winter conditions can suffer. To prevent freezing of the roots, a 20 cm layer of mulch is placed in the trunk circle. Stakes are driven in around the tree, the branches are tied and covered with dense agromaterial.

Breeding technology
Under natural conditions, larch propagates by self-sowing. Seeds are carried by wind or animals. In artificial cultivation, a culture is best propagated by seed method. Experienced gardeners also use cuttings, but the percentage of survival is low. Some sources mention the method of propagation by layering, but it is applicable only to rare weeping species.
Seeds
First of all, the seeds are checked for germination: they are lowered into the water, the dummies will emerge. Then for half an hour the material is soaked in a solution of potassium permanganate to prevent disease. Growing at home requires stratification, i.e., cold hardening. Wet sand is poured into a small container and seeds are placed. The can is kept in the refrigerator for 2 months. Sowing is carried out at the end of April.

Pots or containers up to 300 ml volume with drainage holes are suitable for sowing.
Ideal soil is prepared from the following components:
- high peat 2 parts;
- sphagnum moss 2 parts;
- sand 1 part;
- wood ash 1 part.
The soil placed in the tank must be moistened well, left for a couple of hours, the remaining moisture should be drained from the pallet. Seeds are buried in the substrate by 1.5 cm, in each pot 3-4 seeds. Not all instances can climb, so a surplus is needed.
 Germinate in a well-lit place, covering, if necessary, from direct sunlight. Air temperature + 18 ... + 21 ° С, humidity 65–75%. Seedlings should be protected from drafts and kept away from heating appliances.
Germinate in a well-lit place, covering, if necessary, from direct sunlight. Air temperature + 18 ... + 21 ° С, humidity 65–75%. Seedlings should be protected from drafts and kept away from heating appliances.
Watering is carried out as the soil dries, it should always be moderately moist. Top dressing is carried out the first 3 months every 3 weeks.
Apply:
- the drug "Green Needle", 10 g sprinkle on the ground and pour;
- powder of crushed eggshells, close into the soil and moisten;
- a solution of wood ash in a proportion of 50 g / 5 l, insist 20 minutes, spill the substrate.
Did you know? Larch wood is one of the most resistant to mechanical stress and moisture. This quality has long been used in shipbuilding; some elements of equipment are still being produced.
Feeding can be alternated. In open ground, seedlings are transplanted upon reaching 2 years. At this time, they managed to grow stronger and form the root system. Further care as an adult plant.
Cuttings
Material is harvested in the spring before the movement of juices begins. From last year's branches, shoots are cut to 12 cm long. Seedlings can be rooted immediately in open ground. The bark from the shoot is not cleaned, only the lower part, which will be placed in the soil, is exposed. Stick the stem at an angle of 30-40 degrees.
Germinate in a well-lit place, covering, if necessary, from direct sunlight. Seedlings should be protected from drafts and kept away from heating appliances.
Video: cuttings of larch and other conifers
It is recommended to plant several copies at once, since some may not take root. The area where rooting will be carried out is dug up and fertilized with humus of 4 kg per m². The soil is regularly moistened, soaking it 10 cm deep. For the winter, landing must be carefully covered with mulch, spruce branches and agromaterial. In winter, snow is heaped on top of seedlings.
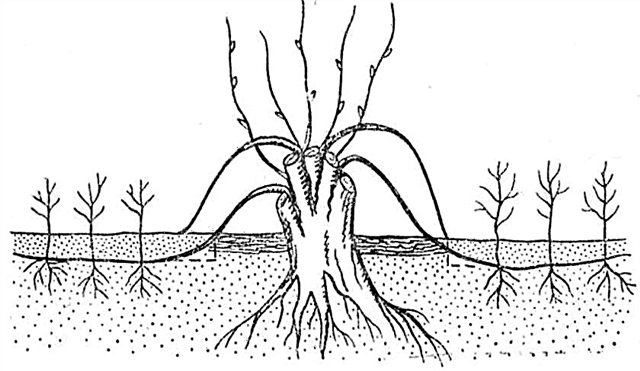
Layering
The easiest way to propagate for weeping varieties of Siberian Larch is to dig layers. In spring, the healthy branch closest to the surface is bent into a previously dug groove. Part of the shoot is dug up and pinned with staples to hold in the ground. Care for the designated sprout is the same as for the mother tree. For winter, a growing seedling requires shelter. It will be possible to cut and transplant the tree in 2 years.
Siberian larch is a beautiful and useful plant that does not require special skills when planting. In the early years, culture is given increased attention, and then it develops, almost independently.