Larches are the most common tree species in the huge boreal forests of Russia and Canada. Larch wood is widely used in construction, and needles, resin and pine cones - in the manufacture of medicines. Read more about what are larch, cultivars, their features and applications, read further in the material.
Types and varieties of larch
The name "larch" (Larix) indicates the genus of trees. It was first described in 1754 by the botanist Philip Miller. The scientist separated pine larch from pine in the family. Now in the scientific literature there are 10-15 species of larch. But not everyone agrees with this. Some botanists divide the genus into 2 parts: Larix - with short bracts and Multiserialis - with long ones. 1 - branch with needles; 2 - a branch with male and female flowers; 3-5 - stamens; 6 - flake, cones; 7 - needles; 8 - section of the cone; 9 - bump; 10-11 - cone flakes; 12 - seed. Others believe that we are talking about simple adaptation of trees to climatic conditions, and there is no need to isolate some of them into a separate subgenus, considering it to be another variety. Larches are the only deciduous conifers. They reach a height of 20–45 m. And, of course, lose needles in the fall, but it does not look like usual leaves, therefore the genus belongs to pine.
1 - branch with needles; 2 - a branch with male and female flowers; 3-5 - stamens; 6 - flake, cones; 7 - needles; 8 - section of the cone; 9 - bump; 10-11 - cone flakes; 12 - seed. Others believe that we are talking about simple adaptation of trees to climatic conditions, and there is no need to isolate some of them into a separate subgenus, considering it to be another variety. Larches are the only deciduous conifers. They reach a height of 20–45 m. And, of course, lose needles in the fall, but it does not look like usual leaves, therefore the genus belongs to pine.
Did you know? The exact origin of the word "Larix" meaning larch is unknown. But there are several versions that the term can refer to tar (Galsk.), Rich (Celtic.), Fat / fat (lat.).
Botanical description of the genus:
- crown shape: cone-shaped, friable, sun rays pass through it well;
- features of the crown: if the area is dominated by winds of one direction, then it becomes uneven, one-sided;
- maximum height: 45-50 m;
- barrel diameter: 1 m;
- shoots: dimorphic, long (from 10 to 50 cm), bearing several buds, and short (1-2 mm);
- leaves: needle-shaped up to 5 cm long, 1 mm in diameter, single, spirally located on long shoots or in clusters of 20-50 needles on short;
- needles texture: soft;
- needles age: one-year;
- cones: straight and small (1–9 cm tall), green, purple or purple in young age, and when ripe, then brown;
- bract scales: may be long or short;
- root system: branched, without a visually distinguished core root, but with many powerful anchor lateral roots, which provide wind resistance of the tree;
- life expectancy: 300–500 years.
The tree loves bright sunny areas. It is steady against winter frosts. But it can be tumbled down if it grows in mossy swamps, that is, where a part of the root is not in solid ground, but in the aquatic environment. Larch grows well on loam and sandy loam soils. In appearance, all species are similar to each other and the difference is only insignificant features noticeable to botanists. Therefore, the name of most of them reflects the region of distribution: Amur, Kamchatka, Seaside, American, Kuril, Polish, Western, Siberian. Another part of the trees is named after the scientist who discovered or described them: Komarov, Middendorf, Lubarsky, Layel, Potanin, Gmelin.
Therefore, the name of most of them reflects the region of distribution: Amur, Kamchatka, Seaside, American, Kuril, Polish, Western, Siberian. Another part of the trees is named after the scientist who discovered or described them: Komarov, Middendorf, Lubarsky, Layel, Potanin, Gmelin.
Common (European)
Common larch (Larix decidua) is also called European or deciduous. This species grows in the mountains of Central Europe, in the Alps and Carpathians, divided by populations on the plains of northern Poland and southern Lithuania. The tree is found in the mountains at an altitude of 2400 m above sea level. Please note that it can only be found in well-drained areas and never in wetlands. European larch is very resistant to cold.
Did you know? The territory on which larch grows in Russia is 5 France (4 billion hectares).
It is able to withstand winter cold to –50 ° C. Cultivated as a decorative tree for planting in gardens and parks. Its strong and durable wood is appreciated in the construction of yachts. From European larch, you can make thin flexible, but durable strips for different purposes. The European species of larch can be called the most diverse.
Among the cultivars obtained on its basis, there are:
- columnar trees whose branches are directed vertically upward (fastigiata);
- plants with drooping branches and apex, which is divided into several others (pendulina);
- multi-stemmed (multicaulis);
- compact or dwarf (stunted) forms;
- creeping shrubs.
There are even those who have one trunk, but it is somewhat winding and then they say that the plant has an indefinite shape. In total, more than 30 varieties have been created on the basis of European larch.
Did you know? The Bullet variety was obtained in the 1990s in Hungary by Josea Miklos. And he named it after his dog.
Here are some of them:
- Horstmann Recurved (Horstmann Recurved) - A very interesting tree, fabulous shape. It is single-barrel, but the trunk may be bent. The branches extending from it are uneven in length and massiveness, bifurcate at the ends, so the crown can be described as pillow-shaped. Height - 2 m. Another feature is the decorative needles. In the spring it is yellow, and by autumn it becomes light brown. The variety was obtained in 2003 by Uwe Horstmann nursery in Germany.

- Kornik (Kornik) - dwarf bush meter high. Looks like a topiary with a sphere-shaped crown on one straight leg.

- Little Bogle (Little Bogle) - a bush with an uneven crown approaching the pyramid, up to 1.6 m high. The owner of the needles is saturated dark green in color, which becomes golden before falling off in the fall. The variety was obtained in 1990 by a nursery in Monbuck (Australia).

- Pendula - larch weeping form with hanging needles. Height - 10-30 m. The crown width of an adult tree is not less than 5 m. For landscape use, Pendulu is grafted onto dwarf fungi to get stunted trees with a weeping crown.
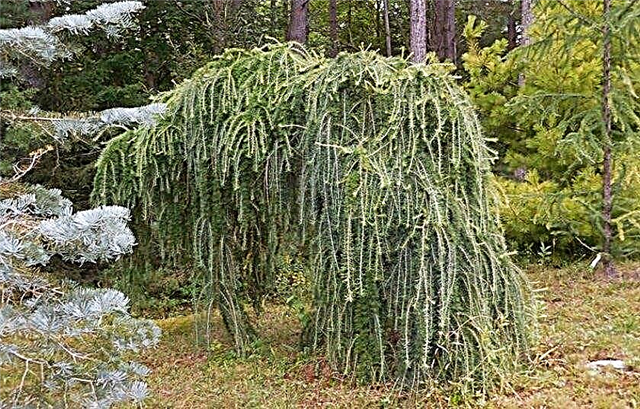

- Pretty Carole (Pritti Carol) - a symmetrical, flattened spherical, European larch with a typical bright, light green needles. It becomes golden before falling in the fall. Height - 1 m. The variety was obtained in 1993 from the variety Lanark (Lanark).

- Repens - larch with creeping shoots. The variety was obtained in England in 1825. It belongs to the dwarf variety and grows to 10 m by 10 years. The annual growth of branches is not more than 15 cm under favorable conditions for development. Given the fact that this larch grows on a stem, its height may vary depending on the properties of the stock. Most often this is a single-barrel tree with a crown in the form of a sphere, but it can also be hanging due to thin, falling shoots. The variety withstands winter temperatures up to –40 ° С. In landscape design, it is used to decorate the entrance to the building. It is allowed to grow not only in open ground, but also in pots for decorating verandas, patios, cafes and urban recreation areas.

- Grade Krejci (Kreichi) - It is considered one of the most unique. Obtained from a deformed sprout by Ladislav Kreichi from Zolakovsky (Czech Republic). This is a slow-growing plant with rare, branching uneven clusters of shoots, the size of which grows by 5 cm per year. This unevenness gives the plant a special charm. The height of a mature larch does not exceed 1 m. The tree is perfect for a rock garden or any Japanese-style garden.

- Puli similar in appearance to the Pendula variety with a hanging (weeping) crown. But it has a denser branching and a lighter shade of foliage. It is considered one of the fastest growing, because the annual growth of its branches is 30 cm. Bullets are a standard tree. It does not take up much space and is very decorative. In November, a veil of Puli branches begins to glare in the sun with bright highlights. And in the spring it again becomes like an elongated green-green bush. The variety should be grown only in the sun on a site with fertile, loose, loamy soil.

Alpine
Alpine larch (Larix lyallii / Alpine larch) was first described in 1863 by Filippo Parlatore. Its synonymous names are French, mountain. The height of the tree is 25 m, the trunk diameter is up to 1.2 m. It is the owner of an irregular rare conical crown. The bark of alpine larch is thin, smooth, yellowish-gray at a young age, with age becomes furrowed and flaky.
Did you know? In the legends of the peoples of the North there is a legend that the gods created the first people from larch. But because of the machinations of evil spirits, it was not larch people that were revived, but clay figures, which is why people became so fragile and short-lived.
Branches grow horizontally, sometimes they are hanging, often twisted and unevenly spaced. They remain on the trunk even after they dry. Deciduous needles growing in bundles from 30 to 40 pcs. Its length is up to 35 mm, thickness - up to 0.6 mm. Seed cones are elliptical in shape, arranged vertically. When appearing, they will be red, then turn purple, turn brown with age. This larch is common in Canada and British Columbia. Frost resistance of wood - up to –34 ° С.
Seaside
Seaside larch (Larix maritima) is a naturally formed hybrid. It is believed that Kamchatka larch crossed with Gmelin or Kayander. It grows in the Khabarovsk Territory, Primorye and in the north of Sakhalin. The tree reaches a height of 25 m. The shoots of the plant are reddish in color with a bluish coating. The shape of the crown is conical. Seaside larch is quite frost-resistant (–40 ° С).
Did you know? Venice is built on piles of larch. Its wood is very dense, not afraid of water and is not subject to destruction for decades.
Siberian
Siberian larch (Larix sibirica) was first described in 1833 by Karl Friedrich von Ledebur. It is also called Russian larch. This tree, reaching a height of 50 m, with a trunk diameter of 1 m. The crown in his youth is conical, but eventually becomes ovoid. The main branches are on the same level with the side branches. Distributed throughout Siberia and the Urals. It is found alone and in groups, it is part of mixed forests, but almost does not form separate forests. Widely used for the production of quality rot-resistant wood. In the state of Oregon (USA), Iseli nursery obtained the only Siberian larch variety, Conica (Konika). It happened in 1990. It is a fast-growing tree with horizontal branches. It is resistant to frost and other adverse factors. By the age of 10, Konika grows to 3 m in height and 1.2 m in width. Its annual growth is 30 cm.
Widely used for the production of quality rot-resistant wood. In the state of Oregon (USA), Iseli nursery obtained the only Siberian larch variety, Conica (Konika). It happened in 1990. It is a fast-growing tree with horizontal branches. It is resistant to frost and other adverse factors. By the age of 10, Konika grows to 3 m in height and 1.2 m in width. Its annual growth is 30 cm.
Video: Siberian Larch
Japanese (Kempfera)
For the first time, Japanese larch (Larix kaempferi / Japanese larch) was described in 1856 by Eli-Abel Carrier. The tree acquired the name “Kempfer” in honor of a botanist who visited Japan one of the first. There, the plant is grown everywhere to obtain strong and durable wood for construction needs. The height of Japanese larch reaches 40 m. The trunk is 7.5 m wide. Its trunk is round, straight, with long horizontal branches.
The crown is conical, dense, becomes irregular and more open with age. The bark is smooth, red-brown, with fissures with age. Needles of gray-green color. Located in a spiral. In the cross section is diamond-shaped. Pollen cones are ellipsoidal in shape, yellow-brown in color, with numerous bracts at the base, 6 mm long, with numerous stamens. Seed cones are straight, with short, curved peduncles. Length - 3 cm, width - 2 cm. When they are immature, they are purple, and as they mature, they become orange-brown. At home, this species grows on different types of soils, including volcanic. But it never appears in swamps and peatlands. The limit of frost resistance of Japanese larch is –28 ° С. This species is also represented by several cultivars.
Length - 3 cm, width - 2 cm. When they are immature, they are purple, and as they mature, they become orange-brown. At home, this species grows on different types of soils, including volcanic. But it never appears in swamps and peatlands. The limit of frost resistance of Japanese larch is –28 ° С. This species is also represented by several cultivars.
Important! Larch needles are used in folk medicine as a hemostatic agent. And resin from it is used to treat wounds, gout, arthritis and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
In the form of a crown of cultivars, breeders tried to preserve and develop the main varieties of the parent variety:
- haptofer - crown of standard conical shape;
- weeping - with decorative hanging shoots.
There are such varieties of Japanese larch:
- Blue Dwarf (Blue Dwarf) - a low bush with one trunk and a spherical crown. By the age of 10, it will grow to only 0.5 m. As a rule, it is grown on a stem, which is why it looks like a tree. Short, highly branched branches make the crown very dense. The diameter of the spherical crown is 80 cm. The variety was obtained in 1982 in the Jan Dieter zu Eddeloch nursery (Germany). The plant is photophilous, frost-resistant and decorative. Plant it on fertile soil in the rock garden or use it to decorate the entrance to the building.
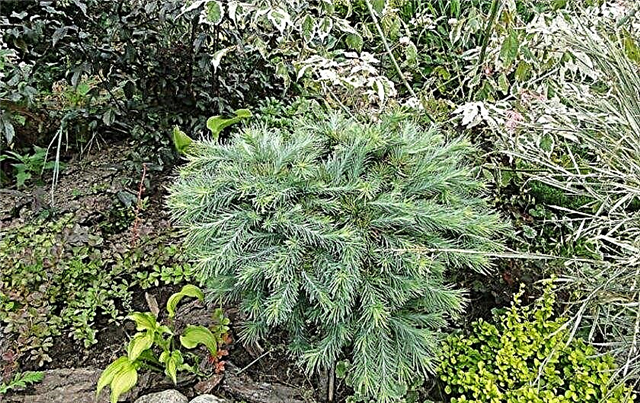

- Grade Blue Rabbit (Blue Rabbit) - unlike the blue dwarf, it is represented by a fast-growing tree of narrow-conical shape and exceptional blue needles. This is probably one of the best varieties with needles of this shade. The height of the adult plant is 3 m and the width is 1.3 m. It was obtained in the Leen Konijn nursery in 1960 in the Netherlands.
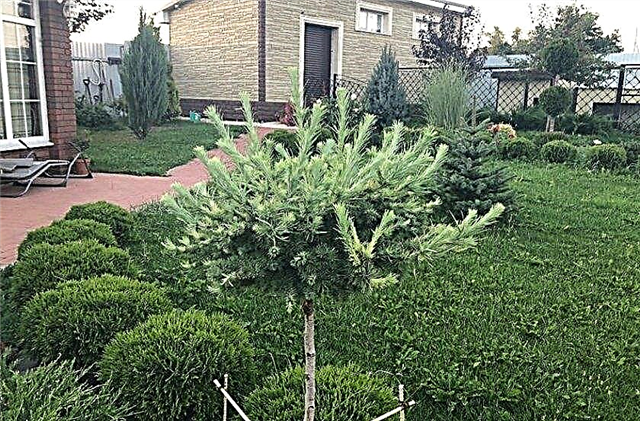

- Diana (Diana) - fast-growing, with curved branches. It is in demand by connoisseurs of non-standard forms. The trunk is curved in the direction of the prevailing wind, the branches are longer on the leeward side, located unevenly. Being of different lengths, they make each tree unique. In adulthood, the conical shape becomes more rounded. The variety was obtained in 1974 in the Gerhard Böhler nursery in Germany. He named it after the Greek goddess of the hunt. Diana is grown on a stem. Reaches a height of 2 m. Very photophilous. It is also important for needles. Bright sunshine helps to reveal its shades as brightly as possible. The variety is recommended for use in the Japanese garden, providing it with fertile and moist soil.
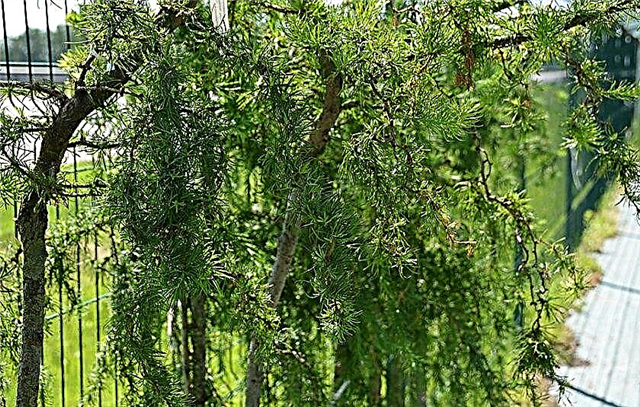

- Jakobsen's Pyramid (Jacobsen Pyramid) - a cone-shaped, almost vertical larch up to 4 m high. A feature of the tree is that its crown from afar resembles poplar - the same narrow pyramidal. This appearance is achieved by the fact that all branches are directed strictly up. The variety was obtained in 1985 in Denmark. The plant prefers a plot with full sunlight and drained soil. It is characterized as a hardy and frost-resistant variety.

- Pendula - one of the most non-standard varieties. Firstly, it is standard, and its height and shape partially depend on the stock. Secondly, it takes various forms depending on the conditions in which it grows. If the crown is not cut, then its hanging branches form a weeping form, descending almost to the ground. Since they are arranged irregularly and are characterized by different lengths, the shape is described as irregular. The variety is considered one of the oldest, obtained around the 1800s. It was first described by the botanist Ludwig Bessner. The height of the plant reaches 7 m, and the diameter of the crown is 3 m. The color of the needles is green-blue. The plant is characterized as frost-resistant, easily adaptable to climate and adverse environmental factors.

American
American larch (Larix laricina) was first described in 1773 by Karl Heinrich Emil Koch. This species is also known under other names: tamarak, eastern, black and red larch. The early settlers in America used its wood as the main building material, as well as for the construction of boats. Today, American larch is growing in Europe, including in the Baltic States, Belarus, Ukrainian Polesie.
Important! Newport Beauty — one of the most demanding varieties. He is prone to sudden larch death syndrome.This is a disease in which a tree dies for no apparent reason. And the older it is, the more prone to illness.
Features of American Larch:
- It is called red because of the pinkish bark. If you lift it, then under it there will be a red layer. Female cones at the beginning of development also have a red color.
- Needle needles, up to 3 cm long, light blue-green color, in the fall it turns bright yellow. It is located spirally on long shoots and in dense clusters.
- Crohn is one of the most elegant. It is small-branched, narrowly pyramidal with open branches.
The tree is ubiquitous in North America. It is very resistant to cold and is able to withstand temperatures up to –65 ° C. It can tolerate a wide range of soil conditions, but more often grows in swamps or moist organic soils, such as sphagnum moss and peat. Also found on mineral soils of any structure: from clay to coarse sand. It can grow on limestone soils. There are fewer varieties of American larch than European, but also enough. This is facilitated by the fact that the plant can be used for the reclamation of marshy lands. It is considered one of the main crops that are able to grow in swamps as pioneer plants, and even in areas with very cold winters.
There are fewer varieties of American larch than European, but also enough. This is facilitated by the fact that the plant can be used for the reclamation of marshy lands. It is considered one of the main crops that are able to grow in swamps as pioneer plants, and even in areas with very cold winters.
The most famous varieties:
- Blue Sparkler - Bred in 1985 by Dr. Sidney Waxman of the University of Connecticut. In the distribution network, it is often mistakenly attributed to varieties of Japanese larch. The tree is characterized by vertically growing branches, light blue needles, which become gray-blue as they age. Like other varieties, it is able to hold drops of water sparkling in the sunshine after rain in leaf axils. For this, a variety in the United States is often called Blue Sparkler. Plant height after 10 years of growth will reach only 1 m, and its annual growth does not exceed 10 m. Blue Sparkler is very popular among landscape designers.

- Deborah Waxman (Deborah Waxman) - Also received at the University of Connecticut in 1988. Dr. Waxman named the variety after his daughter. This is a larch with blue-green sparse needles. Her crown is wide-pyramidal, rather fluffy. It is always decorative. In May, pink cones will appear on the larch, and in the autumn the needles will acquire a shade of copper gold. The tree grows only up to 2 m. The plant is resistant to climate, withstands frosts down to –45 ° С.

- Newport Beauty (Newport Beauty) - A very slowly growing spherical shrub. Its branches are extremely densely located, which makes it resemble a spruce. The beauty of Newport is characterized by bluish-green needles, small height (up to 30 cm), width (60 cm). The variety was obtained in 1988.

- Postus - one of the newest varieties. It was accidentally discovered in Canada and added to the collection of conifers of the Kingsbray Gardens nursery. The tree is characterized by an amazingly narrow pyramidal crown with densely spaced branches. Postus grows very quickly - up to 60–90 cm per year. And this is the highest growth rate among larch trees. It is hardy and withstands frosts down to –45 ° С.
- Stubby (Stubby) - It looks like a dense hill, consisting of branches and needles. It is not very high - only 30 cm in height and in width. In the year, this pillow-like larch grows no more than 2.5–3 cm. Stubby’s needles are of a standard blue-green color. But the variety may be of interest to gardeners due to its low growth.

Decorative pruning of larch
Prepare the tool before trimming. Thin small branches are pruned with pruning shears. Thick - cut down with a saw. The cutting edges of the tool are wiped with alcohol before and after work. This is necessary so as not to transfer phytopathogens from one tree to another. A shaping haircut is necessary to give the crown some shape.
Important! Resin of conifers is poorly washed. Therefore, be sure to wear work clothes and wear gloves when trimming.
In most cases, gardeners preserve plants their natural shape: cone-shaped, spherical, etc. For this, it is enough to cut off branches that are knocked out of this form at the end of winter. Larches are cone-shaped, which means that they can be shaped into a pyramid with tiers, spaces between parts, free from branches, etc.
Step-by-step instructions for forming:
- Examine the tree and imagine the shape you would like to create.
- Remove dry or damaged branches, if any.
- Cut the shoots that rub against each other. If the integrity of the cortex is violated, then phytopathogens can penetrate inside.
- Mark the contours with duct tape, securing the tape to the top and moving from top to bottom. It looks as if you have drawn the outline of a figure.
- Now cut off with the pruner everything that was outlined.
- Remove the tape.
- Be sure to water the tree using a growth stimulator. This is necessary in order to help him overcome the stress of cutting.
- Do not cut more than 1/3 of the green mass, otherwise the plant may die.
 Larch is great for background decoration. Especially if you buy her decorative varieties, not too high. Such forms can be used to design alleys, create flower beds, decorate the entrances to the building or courtyard.
Larch is great for background decoration. Especially if you buy her decorative varieties, not too high. Such forms can be used to design alleys, create flower beds, decorate the entrances to the building or courtyard.